Demystifying Bitcoin: Grasping its Significance and Functionality.
Bitcoin is the currency of the digital age: an international, time-stamped, enduring, and decentralized form of virtual money.
Understanding Bitcoin: A Revolutionary Financial System
Bitcoin, often referred to as a cryptocurrency, is much more than just a digital form of money. It's an innovative technology that has redefined the concept of financial transactions. Built on the principles of transparency and mathematical certainty, it's a system that operates independently, free from the control of any central authority.
This revolutionary protocol was conceived by an anonymous figure known only as Satoshi Nakamoto. Satoshi wasn’t just another tech enthusiast; he was a visionary who saw the need for a trustless payment system in an increasingly digital world. He developed a comprehensive white paper detailing the fundamentals of this novel network.
One aspect that sets Bitcoin apart from traditional currencies is its ingenious solution to a long-standing problem known as “double-spending”. This issue refers to the potential risk of a digital currency being spent more than once, which is essentially equivalent to counterfeiting in the physical world.
“Through advanced cryptographic techniques, Bitcoin effectively prevents double-spending, ensuring the integrity and security of transactions within its network.”
But Bitcoin's use of cryptography doesn't stop at securing transactions. It empowers users with unprecedented financial control and privacy. Your funds are kept secure while your identity remains hidden, giving you peace of mind when making transactions online.
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin facilitate exchange of digital information, enabling users to buy or sell goods and services across the internet without being linked to a real identity. This feature adds another layer of privacy and security for users.
The birth of the Bitcoin network dates back to 3 January 2009 when Satoshi Nakamoto mined the first ever block on the Bitcoin blockchain – the Genesis Block. This block contained a reward of 50 bitcoins, marking the beginning of a new era in finance.
Embedded in this historic block was a message that read:
“The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks.“
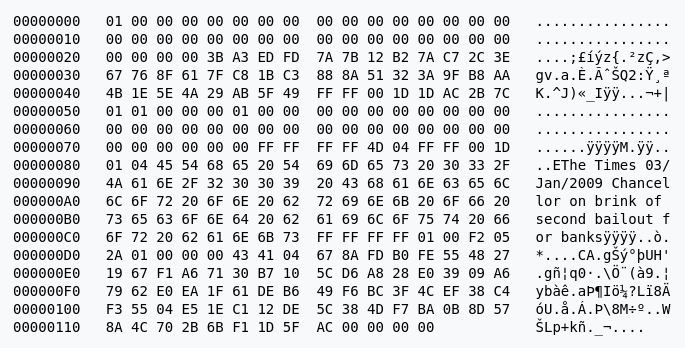
This message, a reference to a headline from ‘The Times' newspaper, cryptically hints at the financial instability of the traditional banking system, thus emphasizing the need for a new, decentralized form of currency – Bitcoin.
Understanding the Purpose of Bitcoin
The Birth of Bitcoin: A Response to Centralization
“Give me control of a nation's money and I care not who makes the laws.”
“I care not what puppet is placed on the throne of England to rule the Empire, …The man that controls Britain's money supply controls the British Empire. And I control the money supply.”
-Mayer Amschel Rothschild, founder of the Rothschild banking dynasty.
These famous quotes underscore the inherent power associated with financial control. They set the stage for understanding why Bitcoin—a decentralized digital currency—came into existence.
Decentralization: The Bedrock of Bitcoin
At its core, Bitcoin's purpose revolves around its decentralized structure. This decentralization puts power back into people's hands. In contrast to centralized systems where all our financial data are managed and updated through centralized servers, decentralization eliminates reliance on third-party entities.
In traditional centralized systems, our data and financial assets are vulnerable to cyberattacks. A successful hack into these systems can have widespread ramifications, including significant economic impact on banks, businesses, and consumers. Furthermore, these institutions have full control over your data and can impose restrictions on transactions.
On the other hand, decentralized networks like that of Bitcoin work differently. Data can be fragmented and encrypted across multiple nodes in the network. Consequently, this creates a secure system where multiple points need to be compromised for an attacker to succeed.
Transparency and Security in Bitcoin
The Bitcoin Source code is completely open-source. This means anyone familiar with coding can review it and participate in its development—nothing is hidden. When you own Bitcoins, your assets are locked on a public ledger (blockchain) and can only be accessed with the correct private keys.
This design ensures no third party such as a bank or institution has control over how many coins you can send or receive, and there is no way they can restrict your transactions. Bitcoin promotes financial freedom.
Bitcoin: Free from Government Interference
Bitcoin is free from government interference and manipulation. Unlike traditional currencies, there’s no Federal Reserve System to hike interest rates. It's also transparent, ensuring that you always know what is happening with your money.
No single institution can counterfeit or arbitrarily create more Bitcoins due to the core rules of the Bitcoin protocol. The inflation rate is programmed into the protocol, and the supply of Bitcoin is capped at 21 million. This means we know exactly how many Bitcoins will ever exist and anyone can verify the total supply of Bitcoin at any given moment.
Embrace the Revolution with Bitcoin
Bitcoin represents a revolutionary technology that's transforming societal norms. Accepting bitcoins is easy—you don't need to invest in setting up merchant accounts or buying credit card processing hardware. And third parties cannot confiscate your wealth without first gaining access to your private keys—essentially, you become your own bank.

Ever wondered why banks impose daily spending limits? That's because they practice “Fractional-Reserve Banking”, which means they don't actually hold all your money in reserve. Here are some useful resources for anyone new to cryptocurrencies:
- Federal Reserve – As the central banking system of the United States, the Federal Reserve plays a crucial role in managing the economy. It's essential to understand its function and influence, especially as Bitcoin stands as an alternative to traditional centralized banking systems.
- Fractional-Reserve Banking – This widespread banking practice involves banks holding only a fraction of their depositors' balances in reserve, lending out the remainder. This concept is significant as it contrasts sharply with Bitcoin's model of full value storage.
- Quantitative Easing – A controversial monetary policy often utilized by central banks to stimulate the economy. Understanding this concept is key to appreciating Bitcoin's deflationary nature.
- Inflation & Deflation – These economic phenomena affect the purchasing power of money over time. They're particularly pertinent given Bitcoin's fixed supply and potential as a hedge against inflation.
- Metcalfe's Law – This principle states that the value of a network is proportional to the square of its users. As Bitcoin continues to gain adoption, Metcalfe's Law becomes increasingly relevant.
- History of the Internet – To fully grasp how revolutionary Bitcoin is, it's useful to understand another transformative technology – the Internet. Drawing parallels between the two can provide intriguing insights.
To delve into the heart of Bitcoin, consider reading The Original Whitepaper. Authored by Satoshi Nakamoto, this document introduced Bitcoin to the world and lays out the foundational principles of this groundbreaking digital currency.
Exploring the Unique Properties of Bitcoin:
Bitcoin, an innovative digital currency, boasts a number of unique and distinct properties setting it apart from traditional currencies.
Decentralization – Bitcoin operates on a decentralized system. Unlike fiat currencies such as dollars or euros that are regulated by central banks, Bitcoin is issued and managed without any central authority. This means no single institution has control over its network.
Digital Nature – Bitcoin is purely digital. Unlike cash or other physical assets, Bitcoin exists solely in the online realm. There are no physical coins or paper bills associated with it, marking a paradigm shift in our understanding of ‘currency'.
Deflationary Aspect – Bitcoin is inherently deflationary. The total supply of Bitcoin is capped at 21 million coins by its underlying protocol. As demand for Bitcoin rises, so does its value – a stark contrast to traditional inflationary currencies where increased supply tends to lower value.
High Divisibility – Bitcoin is highly divisible. One Bitcoin can be divided down to eight decimal places. The smallest unit of a Bitcoin is known as a ‘satoshi', denoted as ₿0.00000001.
Irreversibility – Transactions involving Bitcoins are irreversible by design. Once a transaction is executed, it cannot be reversed unless the recipient agrees to return the Bitcoins. This underscores the importance of double-checking transaction details before executing them.
Persistence – For every transaction, there's a permanent record on the blockchain – an unalterable public ledger – making Bitcoin transactions persistent. Since its inception in 2009, this ledger has remained invulnerable to hacking attempts.
Pseudonymity – In the world of Bitcoin, transactions and accounts aren't tied to real-world identities but to so-called addresses, offering users pseudonymity. However, if an address is ever linked to a real-world identity, all associated transactions could potentially be traced back to that individual.
Borderless Transactions – Bitcoin is borderless. All you need to send or receive Bitcoin is a digital wallet. Transactions are quick, and because they occur over an open network of computers, geographical location is irrelevant.
Permissionless Usage – Bitcoin's permissionless nature allows anyone in the world to participate without needing any form of authorization. Much like the internet, Bitcoin is simply software that can be freely downloaded and used.
Trustless System – Bitcoin operates on a trustless model. You can engage in transactions with strangers without requiring trust, as the system itself ensures integrity and transparency.
Durability – As a peer-to-peer, decentralized form of money, Bitcoin boasts impressive durability. Because it isn't centrally controlled, its resilience mirrors that of the Internet itself – near-infinitely durable.
Security – Bitcoin employs a public key cryptography system for security purposes. Only the owner of the private key associated with a Bitcoin account can authorize transactions, providing robust protection against unauthorized access and fraudulent activities.
Understanding the Functioning of Bitcoin
Bitcoin's remarkable functionality can be attributed to its shared public ledger, known as a Blockchain. This shared public ledger records every single transaction made on the network, forming the backbone of the Bitcoin system.
The Blockchain: A Public Ledger for Bitcoin
In the simplest terms, a blockchain is a diary that is almost impossible to forge. All confirmed transactions are compiled into batches known as blocks. Whenever a new block enters the system, it is propagated across the network of nodes for validation.
This mechanism allows every user to keep track of every transaction, much like how banks maintain physical ledgers. The only key difference is that Bitcoin's ledger is overseen by the public and anyone can access it to verify a transaction.
“Think of it as a transparent and tamper-proof digital ledger.”
Open-Source Nature: Power to Everyone
One of the unique aspects of Bitcoin is its open-source nature. Anyone can download Bitcoin Core, the original software behind Bitcoin, and become a fully validating node in the network. This software adheres to all core rules of the Bitcoin protocol while keeping track of the entire history of transactions on its blockchain.
By downloading the entire blockchain onto your computer, you effectively become an integral part of this vast network:
- You contain all the rules.
- You broadcast transactions.
- You communicate with other nodes.
The more nodes there are in the network, the more decentralized and secure it becomes.
Decentralization: No Single Point of Failure
The Bitcoin network comprises tens of thousands of nodes, each possessing a complete record of all transactions ever made. This decentralized structure eliminates any single point that could potentially be attacked or compromised.
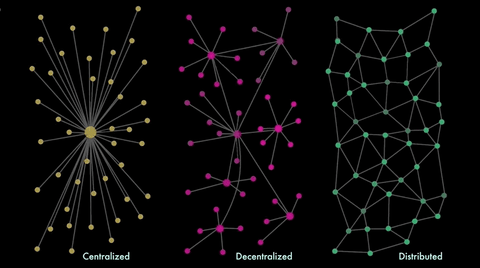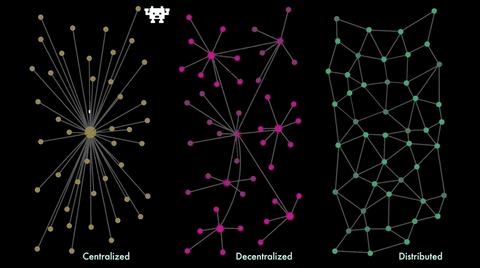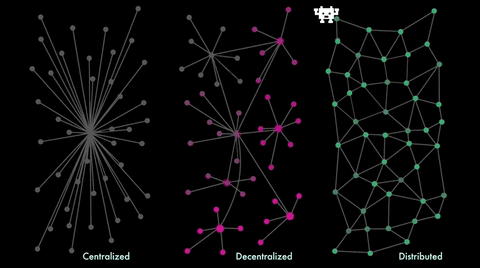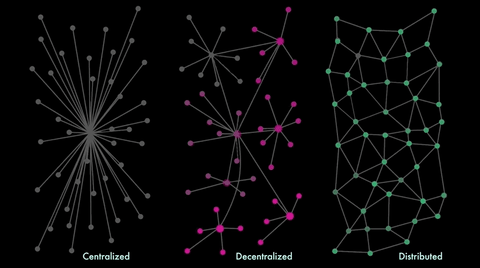
As a result, no institution, bank or government can exert power over Bitcoin or censor it in any way. Indeed, as opposed to traditional fiat currencies like dollars or euros that are controlled by central banks, bitcoins are issued and managed without a central authority.
“Bitcoin exists purely online – decentralized, distributed, and governed by no single entity but maintained collectively by a group of users called miners.
Understanding Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin mining, often described as the backbone of the Bitcoin network, is a complex process that involves several key functions. Its primary roles are to:
- Provide security for the Bitcoin network
- Confirm and validate Bitcoin transactions
This intricate process is performed by specialized hardware known as mining rigs.
The Role of Miners
Miners are responsible for securing new transactions, also referred to as blocks, and queueing them in the blockchain. They accomplish this task by solving a computational math problem. This problem progressively gets more difficult to solve, directly proportional to the number of computers (or nodes) mining on the network.
The greater the number of active miners on the network, the more challenging, secure, and decentralized the network becomes. This not only bolsters the overall integrity of the Bitcoin network but also makes it difficult for any single entity to gain control over it.
As a reward for their service, miners receive newly-created Bitcoins and transaction fees. This system not only ensures a fair distribution of the currency without any central authority but also provides an incentive for more people to take up mining.
Controlled Supply and Block Rewards
The supply of Bitcoin block rewards is strictly regulated by design and agreed upon by all members of the network. The protocol was specifically designed to generate new Bitcoins every ten minutes while halving the mining reward every four years. To counter inflation and maintain value, the total supply of Bitcoins that can ever be created is capped at 21 million. It is projected that the last Bitcoin will be mined in 2140.
The Evolution of Mining Hardware
In its early days, Bitcoin could be mined using a standard home computer. However, as more computers joined the mining pool, solving blocks became increasingly difficult. This necessitated miners to find more efficient ways to mine.
The first major breakthrough was achieved when miners realized they could utilize graphic cards on computers to mine more efficiently. This discovery marked the birth of GPU or Graphics Processing Unit mining.
Soon after, companies began to design specialized machines known as application-specific integrated circuits (ASICS). These machines, specifically designed for mining, are extremely proficient at generating random hashes rapidly.
With the advent of ASICS, Bitcoin mining underwent a major transformation and became a highly industrialized process. Today, it is no longer a viable venture for the average individual due to the substantial investment required in these high-powered machines.
Understanding Bitcoin Wallets
A Bitcoin wallet is the digital equivalent of a traditional bank account. It is your own personal interface to the Bitcoin network, just like your online banking account is an interface to the regular monetary system. It's essentially a tool that allows users to manage their bitcoins, enabling them to send, store, and receive this cryptocurrency with ease.
Key Management in a Bitcoin Wallet
One of the critical functions of a Bitcoin wallet is to manage private keys, which are secret codes that allow you to spend your bitcoins. The concept may be confusing since we're not actually storing bitcoins per se, but rather the private keys that grant you access to them.
Bitcoin addresses and private keys are represented as long strings of numbers and letters or QR codes for simplicity. Here's an example:
Public Key / Address: 13mvq8wD6VxoHrXTVaHPrSwjMwFkYUZxYU
Private Key: 5KMpGa6X1212AmqUd7kdbhevh63Lbt96LU82eQVSSotgFzCGvQ2
Remember, without private keys, you don't have control over your bitcoins. They are the access codes to your Bitcoin address.
How to Verify Your Bitcoin Transactions
You can use any of the following block explorers websites to search any public key online:
These block explorers provide a live view of all Bitcoin transactions happening on the network. It's like an open book of Bitcoin transaction history, allowing you to see how many coins are stored at a particular address and its previous transactions.
Privacy and Transparency in Bitcoin Transactions
Bitcoin operates under pseudonymity. This means that while there is no personal information attached to a Bitcoin address, all transactions are public. Imagine this technology in action in our institutions and banks – governments would no longer be able to fund wars or develop weaponry without public knowledge. Thus, implementing Bitcoin could potentially make the world more transparent while still preserving individual privacy rights.
Types of Bitcoin Wallets
There are four main types of Bitcoin wallets: web, software, hardware, and paper. Each type has its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
- Online web wallets – Web wallets, such as those hosted on cryptocurrency exchanges, offer the lowest level of security due to their online nature. However, they provide the advantage of being accessible from any internet-connected device.
- Software wallets – These wallets can be downloaded and installed on your computers or mobile devices. They strike a balance between convenience and security, making them a great choice for both new and advanced users.
- Hardware wallets – These are physical devices designed specifically for securing crypto coins offline. The three most popular hardware wallets are: Trezor, Ledger and KeepKey.
- Paper wallets – A paper wallet is essentially a piece of paper with your private keys printed on it from an offline computer. This method offers high security but requires caution to prevent loss or damage.
- Understanding these different types of Bitcoin wallets can help you choose the right one for your needs, ensuring secure and efficient management of your Bitcoins.
How to Acquire Bitcoin?
Getting your hands on Bitcoin is simpler than it seems. There are various methods available, primarily buying them, but also through trading services or as payment for products or services. Here are some common ways you can obtain Bitcoin:
Buy Bitcoin with Cash
Purchasing Bitcoin with cash is a straightforward and private method:
- Identify a local Bitcoin ATM or use a peer-to-peer (P2P) exchange like LocalCoinSwap.
- If using an ATM, follow the instructions – typically, this involves scanning your wallet’s QR code and depositing cash.
- For P2P exchanges, locate a seller who accepts cash transactions and arrange a meeting at a secure location.
- After payment is made, confirm receipt of Bitcoin in your wallet.
Please be aware of potentially high rates with this method. For detailed steps, consider The Comprehensive Guide to Buying Bitcoin with Cash.
Buy Bitcoin With Bank Account
Acquiring Bitcoin via bank transfer often provides the best value:
- Choose an exchange that supports bank account transfers like Kraken.
- Verify your identity as per the platform's requirements (this varies based on regional regulations).
- Link your bank account and initiate a transfer to deposit funds into the exchange.
- Once your funds are available, purchase Bitcoin directly on the exchange.
This is a cost-effective approach, though it requires patience for bank processing times. Learn more in The Detailed Guide to Buying Bitcoin with a Bank Account.
Buy Bitcoin with Credit Card
Credit cards offer convenience and speed:
- Select an exchange that accepts credit card payments such as Bybit.
- Complete any necessary identity verification steps.
- Securely add your credit card details within the platform.
- Instantly buy Bitcoin using your card.
Though quick and user-friendly, credit card purchases can incur higher fees and interest charges from card issuers. For further information, review The User-Friendly Guide to Buying Bitcoin with a Credit Cards.
Securing Your Bitcoins
Just like a conventional wallet that holds your cash and credit cards, a Bitcoin wallet is where your bitcoins are stored. It's essential to understand how to keep your bitcoins secure. While it's acceptable to keep small amounts of bitcoins on your mobile device for everyday usage, the majority of your funds should be stored in a safer, more secure environment.
Best Practices for Safeguarding Your Bitcoins
There are several strategies you can employ to ensure the safety of your Bitcoin assets. Here are some key measures to consider:
- Guard Your Private Keys: This is arguably the most critical tip. Your private keys provide access to your bitcoins, much like how a PIN accesses your bank account. As such, these should be kept confidential and secure at all times.
- Master Privacy Protection Techniques: Learn about and employ strategies to protect your privacy when dealing with bitcoins. These could include using VPNs for transactions or ensuring HTTPS encryption during exchanges.
- Avoid Reusing Bitcoin Addresses: Each transaction you make should ideally use a unique address. This prevents potential hackers from tracking your transaction history and patterns.
- Use Separate Wallets for Different Purposes: Just as you wouldn't carry all your cash or cards in one wallet, don't store all your bitcoins in one place either. Diversify across various wallets based on purpose or use case (for instance, savings vs trading).
- Maintain Multiple Secure Backups: Regularly create backups of your wallet and store them in various locations (cloud, hard drive, USB). This way, even if one backup fails or gets compromised, others will still be available.
Investing time in implementing these steps can prevent significant financial loss and give you peace of mind.
Remember: Losing your private key means losing access to your wallet and the bitcoins within. Protect it like you would your most valuable possession.
Final Thoughts: Embracing the Bitcoin Revolution
Bitcoin, a pioneering cryptocurrency, paints a future that stands in stark contrast to our current fiat-based financial system. This potential paradigm shift elicits a gamut of emotions from people worldwide; it's riveting for some, disconcerting for others. The disruptive nature of Bitcoin and its crypto counterparts could significantly reshape numerous markets globally.
However, this brief overview barely scratches the surface of what Bitcoin encompasses. As a highly complex and multi-faceted entity, Bitcoin demands more comprehensive exploration.
To delve deeper into the realm of Bitcoin, consider these high-quality resources that cater to all levels of understanding:
- The original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto offers an in-depth look at the theoretical framework that forms the basis of Bitcoin.
- Developer documentation provides detailed technical information on how Bitcoin functions.
- Wiki covers a broad spectrum of topics related to Bitcoin.
Introducing ‘Bitcoin for Beginners'
Andreas M. Antonopoulos, an acclaimed author, speaker, and educator, stands at the forefront of bitcoin and open blockchain expertise. Known for his electrifying presentations, Antonopoulos masterfully blends economics, psychology, technology, and game theory with current events, personal anecdotes, and historical precedents. His ability to distill complex blockchain concepts into tangible real-world examples has made him a beloved figure in the crypto community.
Through his “Bitcoin for Beginners” series, Antonopoulos aims to demystify blockchain technology and make it accessible to everyone — regardless of their prior knowledge or experience with cryptocurrencies. So, whether you're a novice crypto enthusiast or a seasoned Bitcoin investor, Antonopoulos' insights are sure to provide valuable perspective.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is Bitcoin and why is it significant?
Bitcoin is the currency of the digital age, serving as an international cryptocurrency. Its significance lies in its revolutionary financial system, offering decentralization, transparency, and security.
What are the key features of Bitcoin?
Bitcoin's key features include decentralization, which sets it apart from traditional currencies, as well as its open-source nature and resistance to government interference.
How does Bitcoin function and what is the role of miners?
Bitcoin functions through a decentralized network and relies on miners to secure new transactions and regulate the supply of block rewards.
What are the different types of Bitcoin wallets and how can I acquire Bitcoin?
There are various types of Bitcoin wallets, including web, software, hardware, and paper wallets. Acquiring Bitcoin is relatively simple and can be done through exchanges or peer-to-peer transactions.
How can I ensure the security of my Bitcoins?
To safeguard your Bitcoins, it's important to secure your wallet, employ best practices such as using strong passwords and multi-factor authentication, and stay informed about potential threats.
Who is Andreas M. Antonopoulos and what is ‘Bitcoin for Beginners'?
Andreas M. Antonopoulos is an acclaimed author, speaker, and educator in the field of cryptocurrencies. ‘Bitcoin for Beginners' is an introduction to Bitcoin aimed at those new to the concept.



